Quantum computers could bring lost Bitcoin back to life: Here’s how
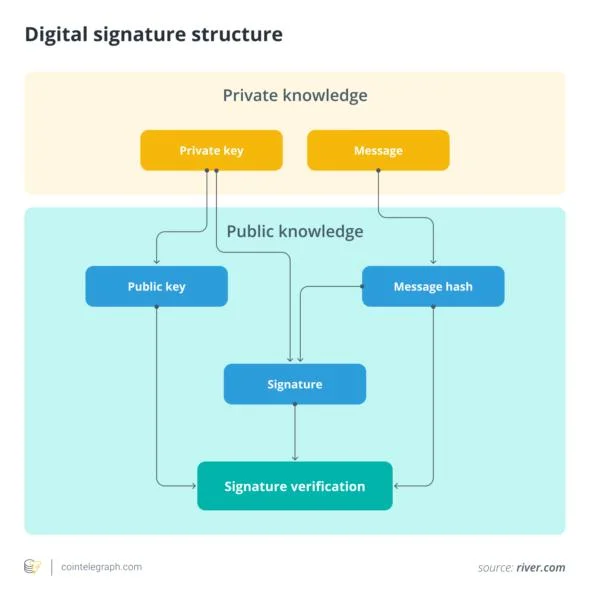
What is quantum technology? Quantum technology can process an enormous amount of data and solve complex problems in seconds rather than decades.Remarkably, quantum technology first appeared in the early 1900s. It originated from quantum mechanics, a branch of physics that examines how matter and energy behave at extremely small scales, such as atoms and subatomic particles. In the real world, it’s applied in modern technologies such as transistors, lasers, MRI machines and quantum computers. These are said to be 300,000 times faster and more powerful than the ones used nowadays. Google’s new quantum chip, Willow, cuts computation times significantly and may provide hackers with the tools to unlock the algorithms that support Bitcoin and other cryptos.Quantum computers could threaten Bitcoin’s cryptographic systems, including the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA). Experts such as Adam Back and Michael Saylor argue that quantum threats to Bitcoin aren’t a concern at present because such applications require advanced quantum hardware, which may take years, if not decades, to develop.Research and development of quantum computers is running at a fast pace, but is Bitcoin quantum-safe at this stage? Not yet, but developers are working to upgrade the network to mitigate possible quantum risks, including breaking encryption.While it’s important to acknowledge the risks, it’s also essential to clarify that these are far from being actual threats for now.Did you know? Albert Einstein made significant contributions to the development of quantum technology. He set the ground for quantum mechanics with his work on the photoelectric effect, which revealed what light is made of. He won the Nobel Prize for this, and not for the relativity theory, as many believe. How quantum tech could break Bitcoin wallets Quantum computing could significantly impact Bitcoin. This is mainly because it could undermine the cryptography that protects its network. Quantum computing and Bitcoin (BTC) have been a hot topic for a while, and rightly so. It can disrupt the network and potentially break Bitcoin wallets by exploiting vulnerabilities in the asymmetric cryptography that secures them. Specifically, the ECDSA, the asymmetric cryptography used in Bitcoin, is vulnerable to attacks by quantum computers. Bitcoin wallets are secured by ECDSA to generate a pair of private-public keys. Its security relies on the hard-to-solve elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem (ECDLP), which is impossible to resolve with classical computers. Bitcoin private key cracking with quantum computers is the real issue since private keys control your Bitcoin. If you lose them, you lose your money. When a private-public key pair is generated, the public key is set for verification, and the private key is for signing.In 1994, mathematician Peter Shor created the Shor quantum algorithm, which can break the perceived security of the algorithms in asymmetric cryptography. All existing algorithms would require a huge amount of time, money and resources to derive a private key from the public key. However, the Shor algorithm will accelerate the process. This means that when a person, organization or anyone with a strong quantum computer will be able to use the Shor algorithm, they may generate a private key from a public one and fake digital signatures for transactions.Bitcoin and quantum security riskYou’ve learned by now that quantum tech could compromise Bitcoin wallets by revealing their private keys. This risk becomes more significant as quantum computers advance, especially for wallets linked to older addresses or those with reused public keys. Quantum computing could make it possible to reverse-engineer private keys from these exposed public keys, threatening the security of Bitcoin holders.In 2025, quantum computers are supposedly decades away from breaking ECDSA. Even Michael Saylor believes the concerns to be unjustified. Bitcoin users can sit back and relax for now, but they should be aware of the best practices to handle any future quantum threats to Bitcoin.Here’s a concise breakdown of the relationship between quantum computing and Bitcoin:Did you know? Quantum computing progress can be assessed by the number of qubits (basic units of information) in one processor. Today, the most powerful quantum computers process between 100 and 1,000 qubits. Estimates for the number of qubits needed to break Bitcoin’s security range from 13 million to 300 million or more. Can quantum computers recover lost Bitcoin? Analysts think that between 2.3 million and 3.7 million Bitcoin is permanently lost. This is about 11%-18% of the total fixed supply of 21 million.What happens to lost Bitcoin when quantum recovery technologies allow dormant wallets to come back to life? Think of Satoshi Nakamoto’s coins alone, which are estimated to be 1 million. If a quantum computer cracks their wallet and releases the coins into circulation, it could lead to big market swings. Quantum computers might bring back that lost Bitcoin by cracking the cryptographic keys that protect those wallets. These are usually wallets with lost or hard-to-reach private keys, making them easy targets.These are likely the oldest versions of Bitcoin addresses, using pay-to-public-key (P2PK) formats, which have never been upgraded or reused. As a result, these addresses remain vulnerable, with no one alive or available to update them. The advancement of quantum computing could potentially exploit these vulnerabilities, unlocking dormant wallets.In May 2025, global asset manager and technology provider BlackRock added a warning to its iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) filing, stating that quantum computing poses a significant risk to Bitcoin’s long-term security due to its ability to break current cryptographic defenses. Ethical and economic implicationsRecovering lost Bitcoin may raise some economic and ethical implications. Reintroducing those coins into circulation could disrupt Bitcoin’s scarcity attribute, and consequently, its market value could be impacted.There are already talks on the best ways to preserve Bitcoin’s economic and ethical value. Many, like OG Bitcoin expert Jameson Lopp, believe those coins should be burned and destroyed forever to protect the network; others believe they should be redistributed for wealth balance. What can you do to protect your Bitcoin? Minimizing the public key exposure is essential if you want to protect your Bitcoin. Simple measures can help users find greater peace of mind.Measures to protect your Bitcoin should always be taken into consideration, regardless of the quantum threats. Fraud is a perennial threat in crypto. Phishing is still one of the most common scams in crypto, with the new zero-value scam revealed, where a phony address is added to the transaction history of a targeted wallet. When the owner starts a transaction, they may simply choose an address from their history and pick the fraudulent one, without even needing to access a private key.Approximately 25% of all Bitcoin is stored in addresses that use pay-to-public-key (P2PK) or reused pay-to-public-key-hash (P2PKH). These methods often reveal the public key linked to a user’s address. This is where the crypto vulnerabilities to quantum computing are more clear since the exposed public keys are more prone to quantum attacks through the Shor algorithm.You can do this by simply avoiding address reuse. Join a platform that helps your wallet change addresses automatically with each transaction. Reusing an address can expose your public key during a transaction.The best you can do is generate new addresses for each transaction and use wallets that support Taproot and SegWit. Don’t forget to pay special attention when you’re sending transactions to your wallet’s addresses. These wallets provide addresses with better security.Address poisoning is another type of common phishing technique that has cost users millions of dollars. It happens when bad actors send small transactions from wallet addresses similar to victims’ legitimate ones, thereby deceiving them by making them copy the wrong address when executing future transactions. Bitcoin’s quantum resistance: Ongoing research and safety measures Bitcoin remains resilient against quantum threats for now, with ongoing research into quantum-resistant wallets and protocols like QRAMP to protect its future, while experts explore ways quantum technology could enhance the network.Bitcoin is decentralized and open-source. Its network adapts well, and ongoing research into quantum-resistant Bitcoin wallets suggests that coins face no immediate threat.Users should follow best practices, like not reusing addresses, to stay safe until quantum-proof cryptocurrencies and wallets are fully ready and available for use.Among the initial measures to protect Bitcoin from quantum threats, Bitcoin developer Agustin Cruz proposed a quantum-resistant asset mapping protocol (QRAMP) in early 2025. It is meant to protect Bitcoin from quantum risks while also allowing Bitcoin to work crosschain, extending to other blockchains without compromising custody or supply limits. Also, experts are developing powerful quantum-resistant cryptographic techniques, which could benefit Bitcoin in several ways. It may improve scalability, create unhackable wallets and strengthen cryptography. These changes will help the Bitcoin network stay strong and thrive in a new quantum world.